Hysterosalpingography
A hysterosalpingography is a type of X-ray that looks at a woman’s uterus (womb) and fallopian tubes (structures that transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus). This type of X-ray uses a contrast material so that the uterus and fallopian tubes show up clearly on the X-ray images.
The radiologist can watch the dye as it moves through your reproductive system and takes radiographs as the dye opacifies and passes through. The doctor will then be able to see if you have a blockage in your fallopian tubes or other structural abnormalities in your uterus.
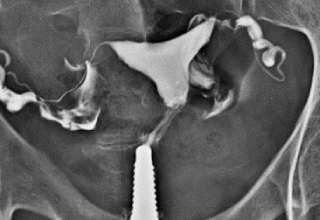
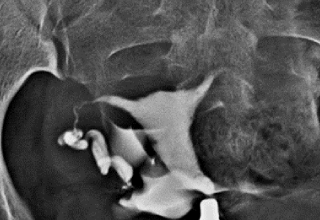
This test requires that you put on a hospital gown and lie on your back with your knees bent and your feet spread, as you would during a pelvic examination. The radiologist will then insert a speculum into your vagina. This is done so that the cervix, which is located at the back of the vagina, can be seen. You may feel some discomfort.
The radiologist will then clean the cervix .Next, an instrument called a cannula will be inserted into the cervix and the speculum will be removed. The radiologist will insert dye through the cannula, which will flow into your uterus and fallopian tubes.
You’ll then be placed under the X-ray machine, and the radiologist will begin taking X-rays. You may feel some pain and cramping as the dye moves through your fallopian tubes. When the X-rays have been taken, the radiologist will remove the cannula.
You’ll then be prescribed any appropriate medications for pain or infection prevention and you will be sent home after an observation of 30 minutes.
This test is usually ordered if you’re having trouble getting pregnant or have had pregnancy problems, such as multiple miscarriages.
Hysterosalpingography can help diagnose the cause of infertility.
Infertility may be caused by:
– Structural abnormalities in the uterus, which may be congenital (genetic) or acquired
blockage of the fallopian tubes
-Scar tissue in the uterus
-Uterine fibroids , tumors or polyps
If you’ve had tubal surgery, a hysterosalpingography is done to check that this surgery was successful. If you had a tubal ligation (a procedure that closes the fallopian tubes), your doctor may order this test to ensure that your tubes are closed properly. The test can also check that a reversal of a tubal ligation was successful in reopening the fallopian tubes.
This test is done ideally in the 1st half of the menstrual cycle 2/3 days after cessation of menses
Ideal time – 7th -10th day
Fasting for 4 hours is preferred.
Reports are issued the same day / next day
Mailing / Whats ap on request
After the test, you may continue to have cramps similar to those experienced during a menstrual cycle. You may also experience vaginal discharge or slight vaginal bleeding. You should use a pad instead of a tampon to avoid infection during this time.
Some women also experience dizziness and nausea rarely vomiting during or after the test. These side effects are normal and will eventually go away.
However, let your doctor know if you experience symptoms of infection, including:
Complications from a hysterosalpingography are rare. Possible risks include :
| Test timing | Patient Preparation | Pre-procedure Medication | Test duration | Common Indications | Risks and complications | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSG (Hysterosalpingography) | Anytime during the day, 7th to 10th day of menstrual cycle, Prior appointment required | Fasting for 2-3 hrs, Inform the doctor about allergies to any medicines, latex, or anesthetics and about existing medical conditions. Remove all jewelry and aids or devices such as dentures, hair clips etc; and wear a hospital gown. Let your doctor know about all the medicines you are currently taking, Carry all your relevant old reports and show it to the doctor before the test | Prophylactic antibiotics before or after the test to prevent infection; SOS Atropine inj IV /IM and a Tetanus toxoid injection | 30 mins | Infertility, Diagnose fallopian tube blockage, Adhesions in uterus, After tubal ligation / tubal ligation reversal | Rare. Possible risks include- Allergic reaction to contrast dye, Endometrial (uterine lining) or fallopian tube infection, Injury to the uterus, such as perforation |
A barium X-ray is a radiographic (X-ray) examination of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Barium X-rays (also called upper and lower GI series) are used to diagnose abnormalities of the GI tract, such as tumors, ulcers and other inflammatory conditions, polyps, hernias, and strictures.
Barium is a dry, white, chalky powder that is mixed with water to make barium liquid. Barium is an X-ray absorber and appears white on X-ray film. When instilled into the GI tract, barium coats the inside wall of the esophagus, stomach, large intestine, and/or small intestine so that the inside wall lining, size, shape, contour, and patency (openness) are visible on X-ray. This process shows differences that might not be seen on standard X-rays.
Barium is used only for diagnostic studies of the GI tract.
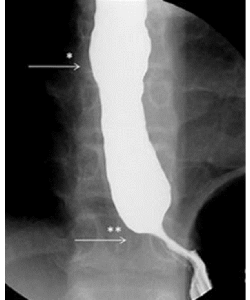
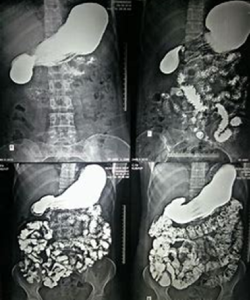
This test is done any day of the month.
| Test timing | Patient Preparation | Test duration | Common Indications | Risks and complications | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barium Swallow | Anytime during the day, Prior appointment required | Fasting for 2 hrs, Inform the doctor about allergies to any medicines, latex, or anesthetics and about existing medical conditions. Remove all jewelry and aids or devices such as dentures, hair clips etc; and wear a hospital gown. Let your doctor know about all the medicines you are currently taking, Carry all your relevant old reports and show it to the doctor before the test | 30 mins | Difficulty in swallowing, Gastro-oesophageal reflux, Hiatus hernia, Oesophageal spasm | Constipation or impacted stool, Trouble with bowel movements, Inability to have a bowel movement or pass gas, Pain or swelling of the abdomen, Allergic reaction or anaphylaxis to the barium drink, Barium aspiration in the windpipe |
| Barium Follow-through | Early morning, Prior appointment required | Overnight fasting, Laxatives ( 2 tabs Dulcoflex)previous night for bowel clearance, Inform the doctor about allergies to any medicines, latex, or anesthetics and about existing medical conditions., Remove all jewelry and aids or devices such as dentures, hair clips etc; and wear a hospital gown. Let your doctor know about all the medicines you are currently taking, Carry all your relevant old reports and show it to the doctor before the test | 2-4 hrs | Constipation or impacted stool, Trouble with bowel movements, Inability to have a bowel movement or pass gas, Pain or swelling of the abdomen, Allergic reaction or anaphylaxis to the barium drink |
Reports are issued the same day / next day
Mailing / WhatsApp on request
An intravenous pyelogram, also called an excretory urogram, is an X-ray exam of your urinary tract.
An intravenous pyelogram lets your doctor view your kidneys, bladder and the tubes that carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder (ureters).
An intravenous pyelogram may be used to diagnose disorders that affect the urinary tract, such as kidney or ureteric stones, bladder stones, enlarged prostate, kidney cysts or urinary tract tumors.
During an intravenous pyelogram, an X-ray dye (iodine contrast solution) is injected into a vein in the arm. The dye flows into your kidneys, ureters and bladder, outlining each of these structures. X-ray pictures are taken at specific times during the exam, so the doctor can clearly see your urinary tract.
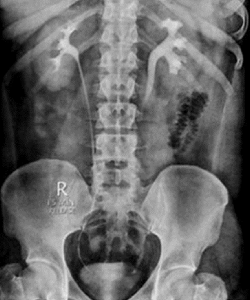
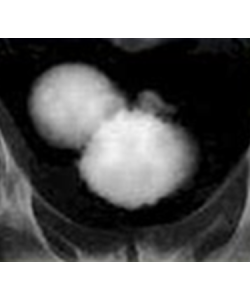
This test is done any day of the month.
Reports are issued the same day / next day
Mailing / WhatsApp on request
WhatsApp us
Request An Appointment
To schedule an appointment please contact our office by phone or by filling in the form below and we will get back to you